Daily Quizzes
Mock Tests
No tests attempted yet.
Select Category
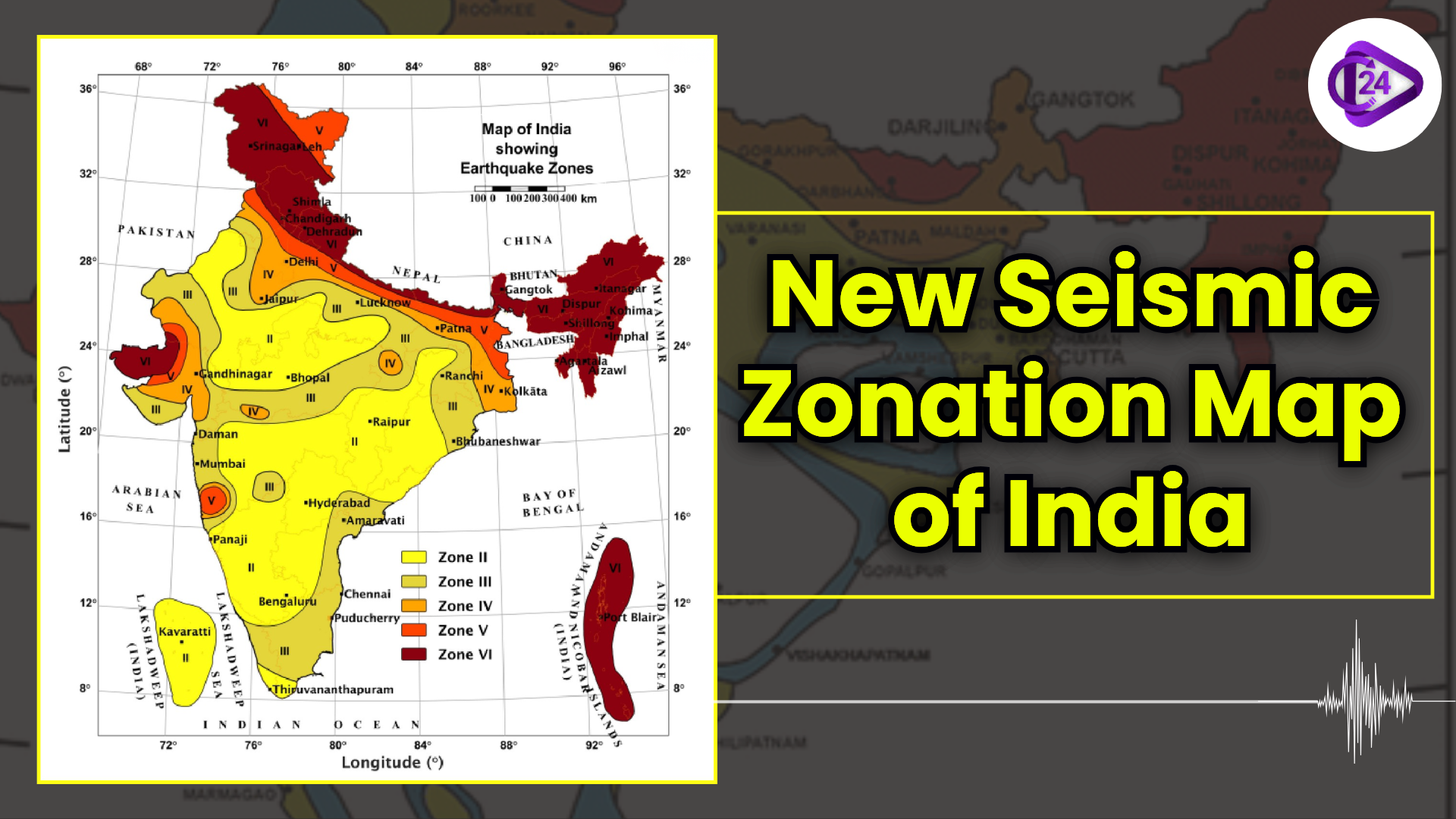
Previously, the Indian landmass was defined into four earthquake zones, including Zones II, III, IV, and V.
Adds a new highest risk Zone VI, with the whole Himalayan arc being covered by that new Zone VI for the first time. Zonal constraints: This is now automatically classified as higher risk. Hazard mapping: This gives importance to geological conditions rather than administrative boundaries.
India’s Earthquake Vulnerability
-
The number of moderate to high seismic hazard areas (previously 59 percent) is 61 percent of the territory of India.
-
An area of 75 percent of India's population is in the seismically active areas.
-
Promotes retrofit of the old buildings in risky regions.
-
Prohibits building in soft sediments or active fault lines.
-
Encourages the implementation of the standard building codes in the Himalayan and other vulnerable areas.
-
NDMA establishes federal disaster management policies.
-
Disaster plans at the state level are developed and executed by SDMAs.
-
The National Seismological Network keeps watch on earthquake activities in India.
-
Study of early warning systems of earthquakes.
Previous Year Question Based on Earthquake Zone
| Exam & Year | Question | Options | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| UPSC Prelims 2023 | Which of the following percentages of India’s land falls in high seismic zones according to the updated map? | A. 10% B. 20% C. 30% D. 40% |
C. 30% |
| SSC CGL 2022 | India is divided into how many seismic zones as per BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards)? | A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6 |
C. 5 |
| RRB JE 2021 | Which region of India falls under the highest seismic hazard zone? | A. Indo-Gangetic plains B. Himalayan region C. Western Ghats D. Deccan plateau |
B. Himalayan region |
| UPSC Prelims 2021 | The National Seismological Network in India is responsible for? | A. Monitoring earthquakes B. Flood control C. Cyclone prediction D. Soil erosion studies |
A. Monitoring earthquakes |
| SSC CHSL 2020 | Earthquake-prone zones of India are classified on the basis of? | A. Population density B. Seismicity and past earthquake records C. Rainfall D. River systems |
B. Seismicity and past earthquake records |
| State PCS 2019 | Which authority is responsible for implementing disaster management plans in Indian states? | A. NDMA B. SDMA C. ISRO D. NDRF |
B. SDMA |
| UPSC 2018 | National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) functions under which ministry? | A. Ministry of Home Affairs B. Ministry of Earth Sciences C. Ministry of Defence D. Ministry of Environment |
A. Ministry of Home Affairs |
Expected Questions for Seismic Zone of India
Question 1: Which zone on the earthquake map of India represents the highest seismic risk?
a) Zone II
b) Zone III
c) Zone V
d) Zone VI
Answer: d) Zone VI
Description: Zone VI (dark brown colour) indicates areas of very high seismic risk, including parts of the Himalayas, Northeast India, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
Question 2: Which major city falls under Zone V?
a) Delhi
b) Jaipur
c) Mumbai
d) Bengaluru
Answer: a) Delhi
Description: Zone V (red color) represents high seismic hazard areas, including Delhi, Patna, and parts of Gujarat and Maharashtra.
Question 3: Which state in India is entirely in Zone II (low seismic risk)?
a) Gujarat
b) Karnataka
c) Kerala
d) West Bengal
Answer: b) Karnataka
Description: Zone II (yellow) indicates low seismic hazard, covering most of southern India, including Karnataka, Kerala, and parts of Andhra Pradesh.
Question 4: Port Blair in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands falls under which earthquake zone?
a) Zone III
b) Zone IV
c) Zone V
d) Zone VI
Answer: d) Zone VI
Description: The Andaman & Nicobar Islands are in Zone VI due to their location near tectonic plate boundaries, making them highly prone to earthquakes.
Question 5: The city of Mumbai falls under which earthquake zone?
a) Zone II
b) Zone III
c) Zone IV
d) Zone V
Answer: d) Zone V
Description: The western coast of India, including Mumbai, is in Zone V, which indicates a high risk of earthquakes.
Question 6: Which of the following cities is in a moderate-risk zone (Zone III)?
a) Bhopal
b) Jaipur
c) Hyderabad
d) Shillong
Answer: c) Hyderabad
Description: Zone III (light yellow-brown) represents moderate seismic risk, including Hyderabad, Chennai, and parts of central India.
Question 7: Which of the following states has areas in both Zone IV and Zone V?
a) Gujarat
b) Maharashtra
c) Rajasthan
d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer: a) Gujarat
Description: Gujarat has regions in Zone IV (orange) and Zone V (red), reflecting both moderate and high seismic risk areas.
Conclusion
The recent 2025 Seismic Zonation Map of India re-establishes the risk of an earthquake with the whole Himalayan belt in the Zone of highest risk of VI. Moderate-to-high hazard (61 percent of the landmass in India) covers safer urban planning, stricter building codes, and better disaster preparedness; planning infrastructure and policies to match the seismic assessment of science.



 Goa Set to Release Its First Biodiversity and Culture Map
Goa Set to Release Its First Biodiversity and Culture Map Gujarat Becomes India's No. 1 Renewable Energy Contributor
Gujarat Becomes India's No. 1 Renewable Energy Contributor Global Water Bankruptcy Report
Global Water Bankruptcy Report Mumbai To Host India's First City-Led Initiative To Showcase Climate Action
Mumbai To Host India's First City-Led Initiative To Showcase Climate Action Biologist Toby Kiers Wins Tyler Prize for Revealing Fungal Networks
Biologist Toby Kiers Wins Tyler Prize for Revealing Fungal Networks Why Protecting the Aravalli Range Matters for Climate, Water, and Biodiversity
Why Protecting the Aravalli Range Matters for Climate, Water, and Biodiversity Supriya Sahu Wins UNEP Champions of the Earth 2025
Supriya Sahu Wins UNEP Champions of the Earth 2025 World Soil Day 2025: Celebrating “Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities”
World Soil Day 2025: Celebrating “Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities” Cyclone Fina Hits Northern Australia With Destructive Force
Cyclone Fina Hits Northern Australia With Destructive Force






