Daily Quizzes
Mock Tests
No tests attempted yet.
Select Category

Toby Kiers, an American evolutionary biologist, has won the 2026 Tyler Prize in Environmental Achievement, sometimes referred to as the Nobel Prize in the Environment. The work by Kiers has demonstrated the existence of the mycorrhizal fungi creating networks among plant roots, influencing the fungal process of exchange, capturing about 13 billion tonnes of carbon every year, and forming the foundation of biodiversity and climate stability. She is also the co-founder of the Society for the Protection of Underground Networks (SPUN), where she is utilising her prize platform to further fungal science, conservation, and policy globally.
Tyler Prize 2026: Toby Kiers’ Climate Breakthrough
-
Toby Kiers, an evolutionary biologist, was awarded the 2026 Tyler Prize in Environmental Achievement because he discovered the significance of underground fungal networks in climate and ecosystem health.
-
In her studies, she demonstrates that mycorrhizal fungi globally connect the roots of plants and serve as the means of interacting with nutrients and sequestration of an estimated 13 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide each year.
-
The networks are vital to biodiversity, soil health, and climate resilience.
-
Kiers went on to co-found the Society for Protection of Underground Networks (SPUN) to survey and preserve these systems, as well as lobby for these systems and get them included in the conservation policy.
-
An award of 250k is also part of the prize, bringing attention to her contribution to global environmental science and policy.
Expected MCQs on Tyler Prize
Q. When was the Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement first established?
A) 1970
B) 1973
C) 1980
D) 1985
Answer: B) 1973
Explanation: The Tyler Prize was established in 1973 to recognise individuals or organisations making outstanding contributions to environmental science, energy, and health.
Q. Who was the first recipient of the Tyler Prize?
A) Rachel Carson
B) Barry Commoner
C) Paul Ehrlich
D) Jane Goodall
Answer: B) Barry Commoner
Explanation: Barry Commoner, an American biologist and ecologist, was the first recipient for his work on pollution and ecological awareness.
Q. Where is the Tyler Prize awarded?
A) Washington, D.C.
B) New York
C) Los Angeles
D) San Francisco
Answer: C) Los Angeles
Explanation: The Tyler Prize ceremony is held in Los Angeles, United States.
Q. Which organisation administers the Tyler Prize?
A) United Nations Environment Programme
B) University of Southern California (USC)
C) Environmental Protection Agency
D) National Geographic Society
Answer: B) University of Southern California (USC)
Explanation: The Tyler Prize is administered by USC’s Institute of the Environment and Sustainability.
Q. What is the main purpose of the Tyler Prize?
A) To award achievements in medicine
B) To recognise contributions in environmental science, energy, and health
C) To award innovation in technology
D) To recognise humanitarian work
Answer: B) To recognise contributions in environmental science, energy, and health
Explanation: The Tyler Prize honours groundbreaking work that benefits the environment, public health, and sustainable development.
Q. How often is the Tyler Prize awarded?
A) Annually
B) Biennially
C) Every five years
D) Every two years
Answer: A) Annually
Explanation: The Tyler Prize is presented once every year to one or more individuals or organisations.
Q. Who selects the Tyler Prize winners?
A) United Nations Panel
B) Committee of environmental experts appointed by USC
C) General public voting
D) US Congress
Answer: B) Committee of environmental experts appointed by USC
Explanation: Winners are chosen by an expert advisory committee focused on environmental achievement and sustainability impact.

Conclusion (Biologist Toby Kiers Wins Tyler Prize)
The 2026 Tyler Prize given to Toby Kiers demonstrates the importance of fungal networks in the underground in global biodiversity and climate regulation. Her groundbreaking work in the field of mycorrhizal fungi not only increases environmental science but also paves the way to policy, conservation, and awareness of the importance of fungi in the maintenance of the ecological systems across the globe.



 Goa Set to Release Its First Biodiversity and Culture Map
Goa Set to Release Its First Biodiversity and Culture Map Gujarat Becomes India's No. 1 Renewable Energy Contributor
Gujarat Becomes India's No. 1 Renewable Energy Contributor Global Water Bankruptcy Report
Global Water Bankruptcy Report Mumbai To Host India's First City-Led Initiative To Showcase Climate Action
Mumbai To Host India's First City-Led Initiative To Showcase Climate Action Why Protecting the Aravalli Range Matters for Climate, Water, and Biodiversity
Why Protecting the Aravalli Range Matters for Climate, Water, and Biodiversity Supriya Sahu Wins UNEP Champions of the Earth 2025
Supriya Sahu Wins UNEP Champions of the Earth 2025 World Soil Day 2025: Celebrating “Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities”
World Soil Day 2025: Celebrating “Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities”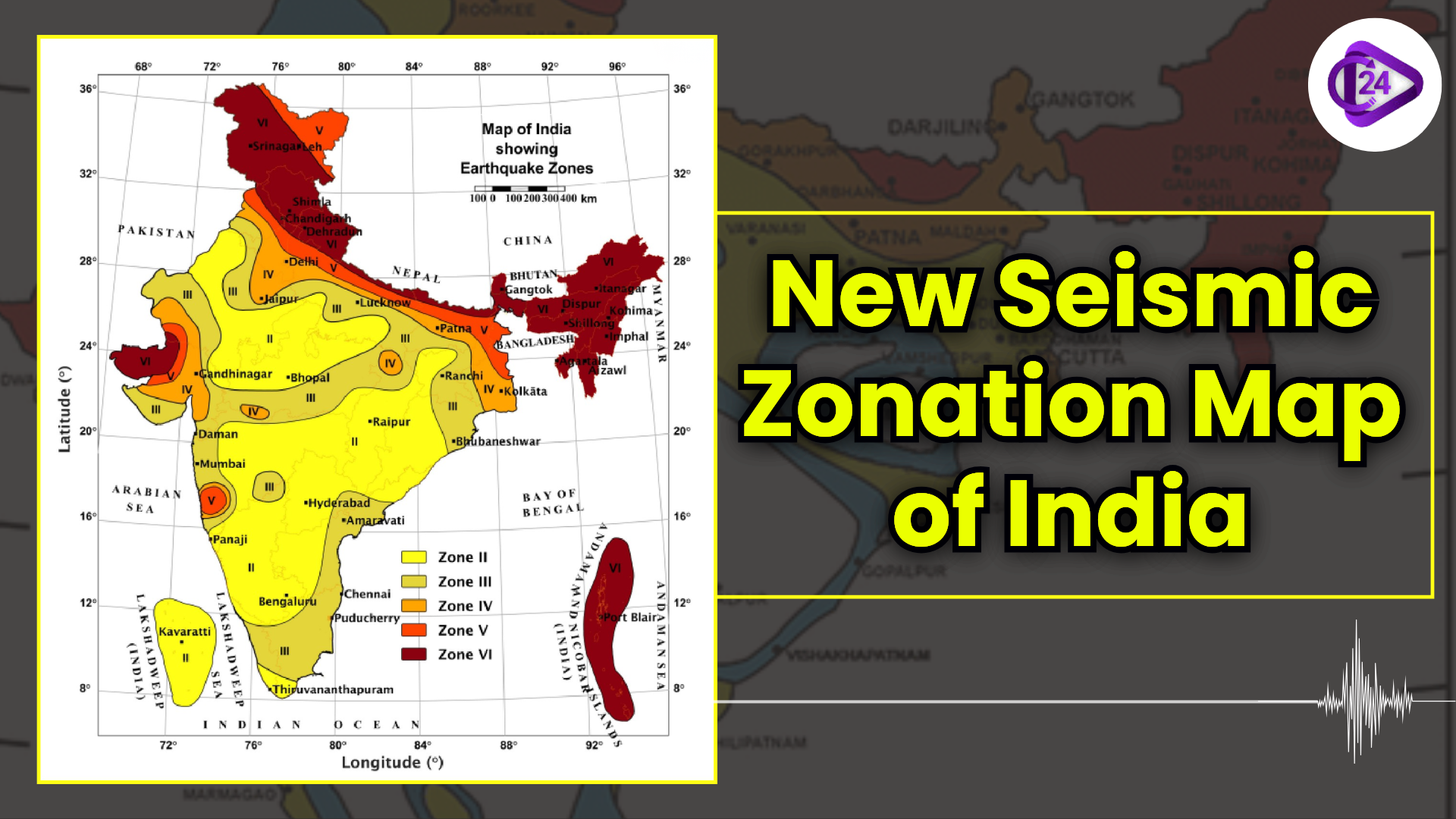 New Seismic Zonation Map of India
New Seismic Zonation Map of India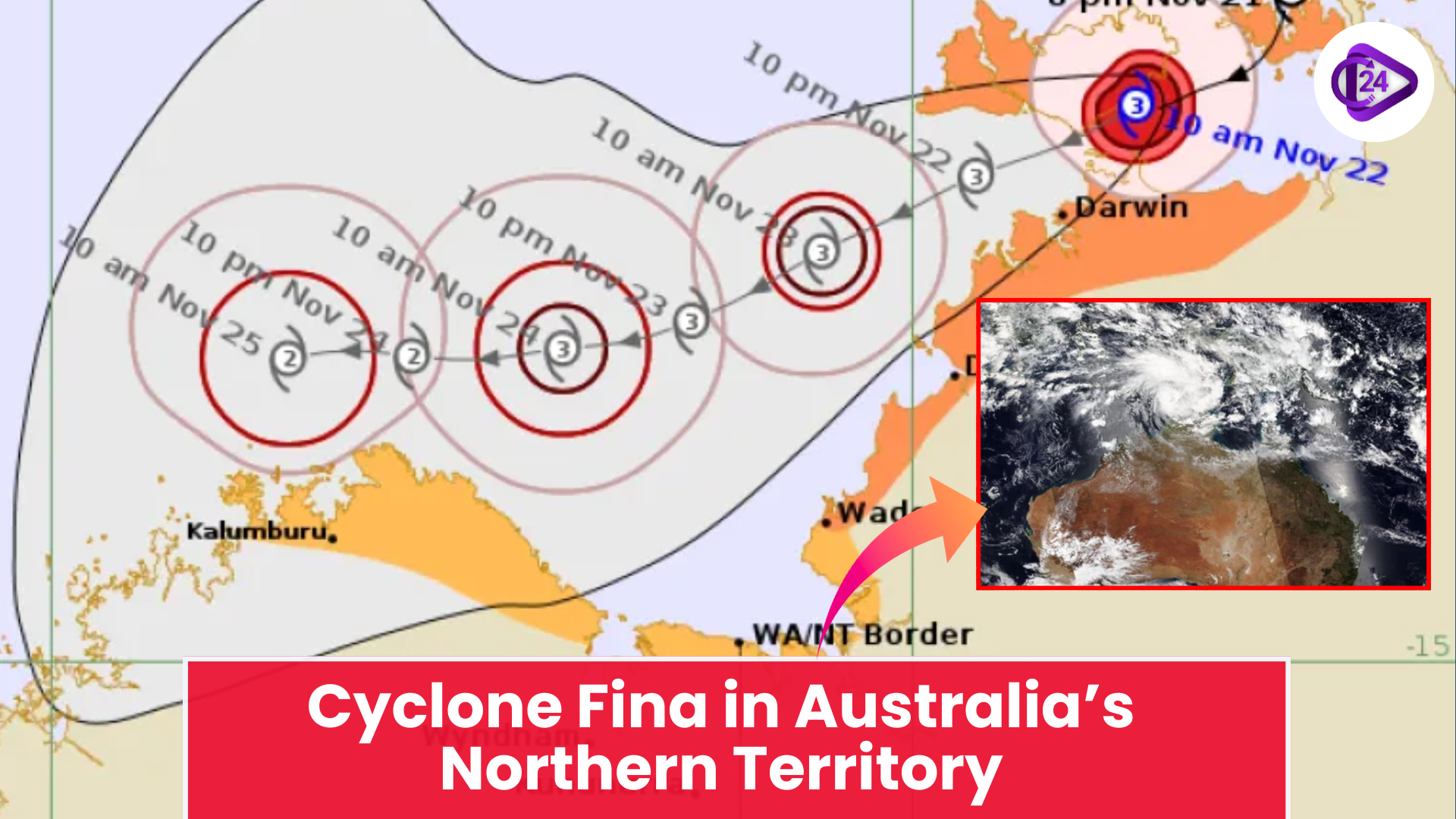 Cyclone Fina Hits Northern Australia With Destructive Force
Cyclone Fina Hits Northern Australia With Destructive Force






