Daily Quizzes
Mock Tests
No tests attempted yet.
Select Category
The Human Heart: A Complete Guide to Structure, Function, and Importance.
The human heart is an interesting and essential organ, working day and night to keep the body active. As the main organ of the circulatory system, it is the driving force that drives blood movement as it provides oxygen and nutrients to all the body's cells.
The human heart functions throughout life and is one of the strongest and hardest-working muscles in the human body.
In addition to humans, most other animals also have a heart that pumps blood throughout their bodies. Even invertebrates like grasshoppers have a heart-like pumping organ, although they do not function like the human heart.
Introduction The Heart -The Lifeblood of Life
The heart has been termed by many as the most important organ in the human body, as it is the one that . In the absence of this repeated cycle, tissues would soon be starving due to lack of oxygen and nutrients, and death will occur.makes blood flow all over the body to keep the body alive. Its main role is to circulate blood in the arteries to the organs and tissues as well as to pump deoxygenated blood in the body to the lungs to be oxygenated
Its purpose is very obvious, but the internal structure of the heart is very complicated as it is adapted to carry out its task very efficiently. The heart exists in the thoracic cavity and is closely connected to blood vessels, veins, and arteries in order to ensure the blood circulation is the best.
Position of the Human Heart
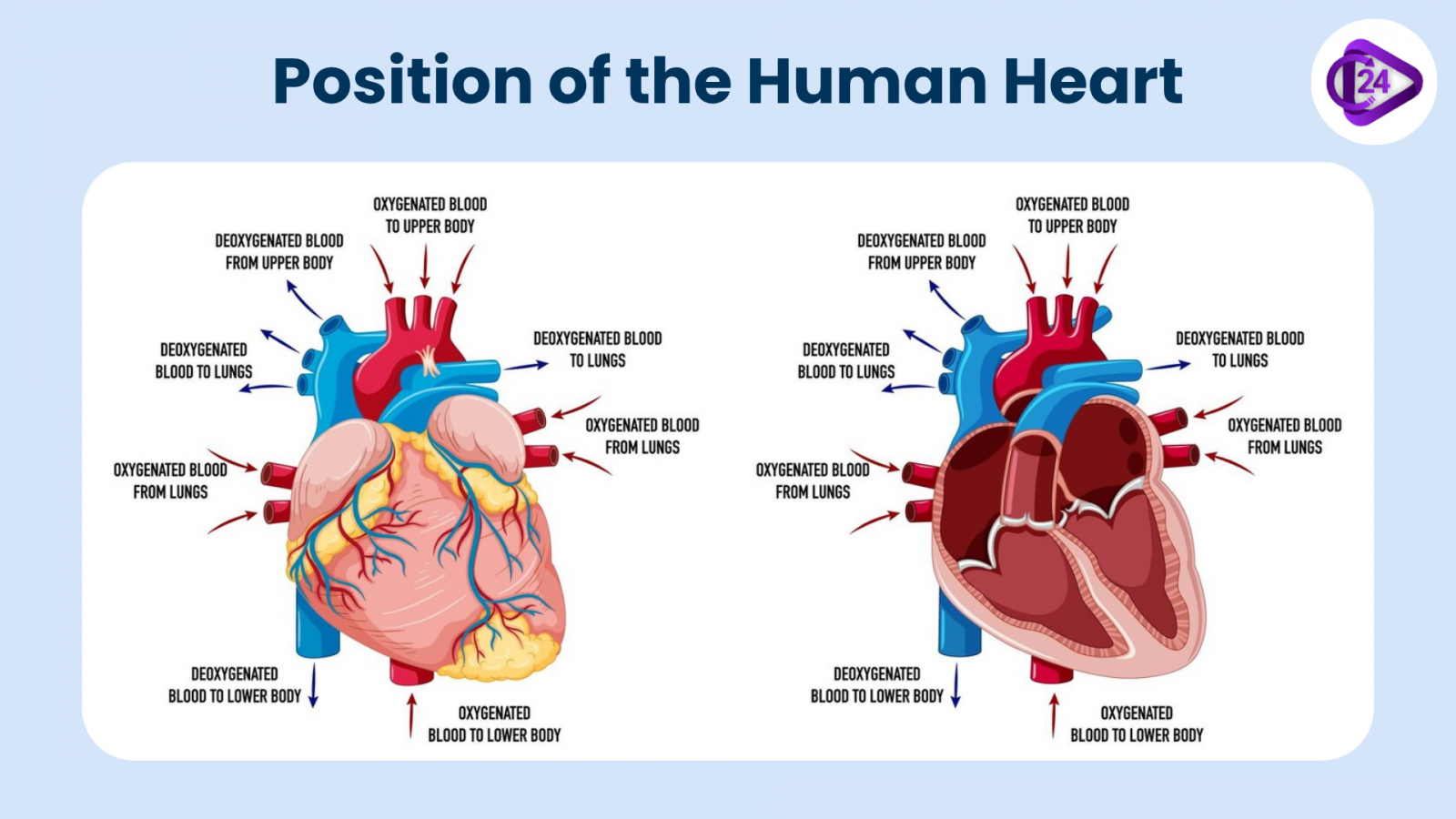
The human heart is located slightly to the left of the center of the chest, nestled between the two lungs, and resting in a cavity known as the mediastinum. This positioning ensures that the heart is protected by the rib cage while still being able to pump blood to all parts of the body efficiently. The apex of the heart points downward, toward the left, while the base lies at the upper part of the organ and points towards the right shoulder.
The average weight of the human heart is about 250-300 grams for women and 300-350 grams for men. It is roughly the size of a fist and is enclosed by a protective sac called the pericardium, which we will explore in more detail later.
Functions of the Human Heart
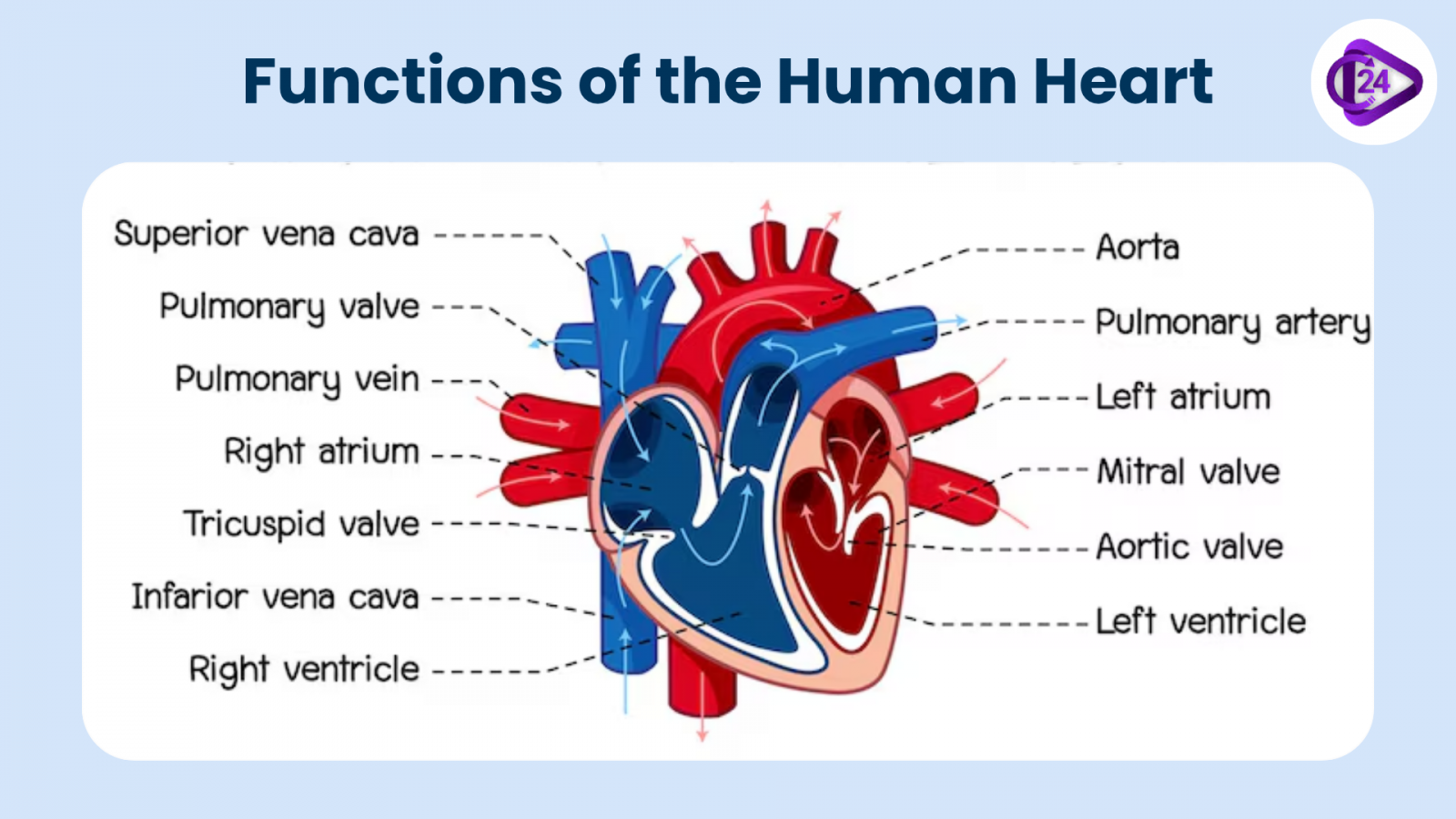
The heart has many important functions in the body all of which are associated with blood transportation. Its major areas of responsibility are:
- Pumping Oxygenated Blood: This is a pumping process in which the left side of the heart pumps in blood that contains oxygen to the rest of the body to ensure that cells obtain the nutrients required to operate.
- Pumping Deoxygenated Blood: The heart pump of the right side forces the deoxygenated blood to the lungs where oxygen can be absorbed and carbon dioxide is eliminated.
- Keeping Blood Pressure: This is a process wherein the contraction and relaxation of the heart takes place in rhythm to the required blood pressure in the blood vessels to propel the blood in the body.
- Supporting Circulatory Systems: The heart is supported by two large circulatory systems called systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation that we shall presently discuss in further detail
Types of Circulation
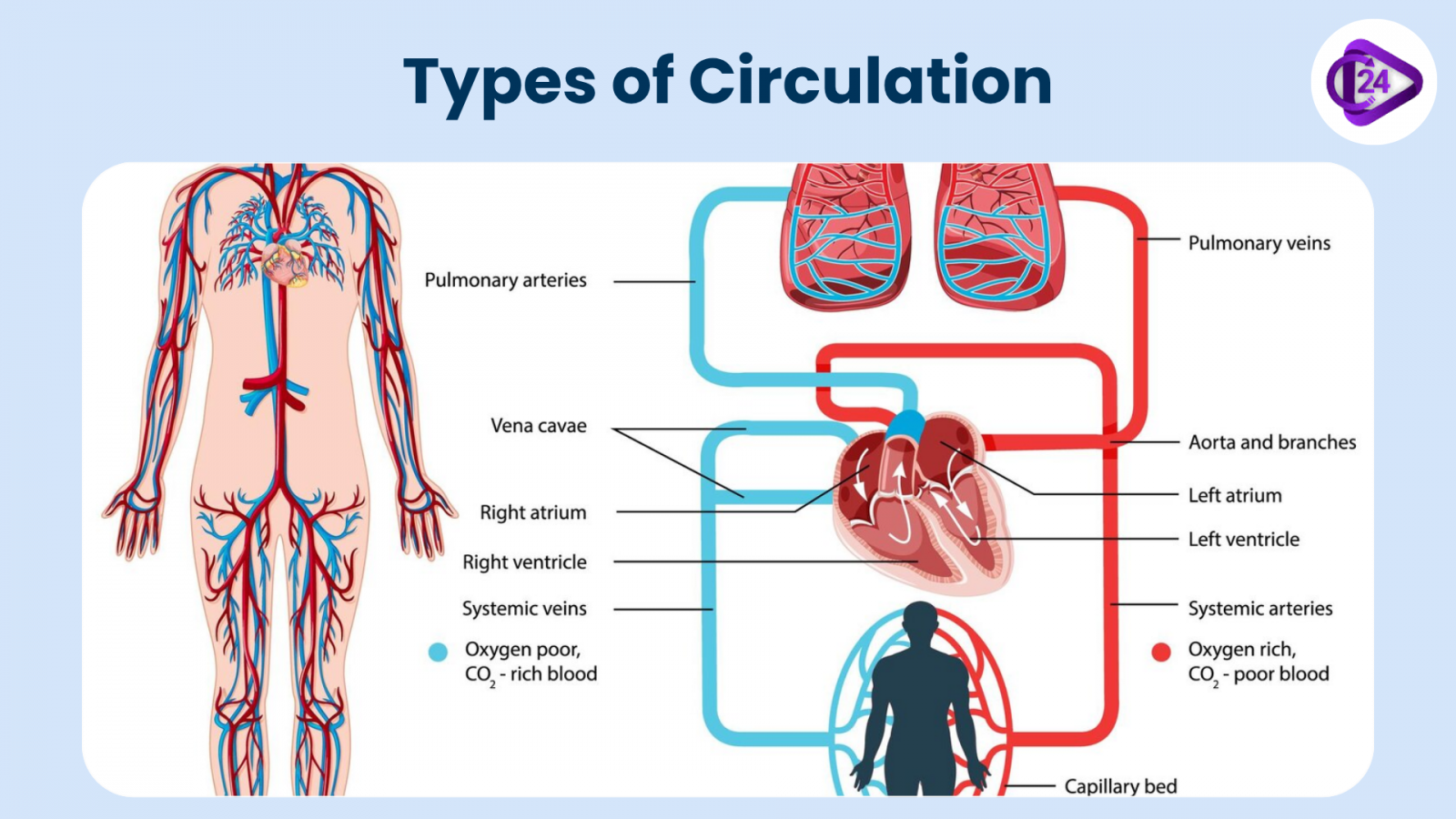
There are two main circulatory pathways that the heart supports: systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation.
- Pulmonary circulation is a portion of circulation responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs and then bringing oxygenated blood back to the heart.
- Systemic circulation is another portion of circulation where the oxygenated blood is pumped from the heart to every organ and tissue in the body, and deoxygenated blood comes back again to the heart.
Now, the heart itself is a muscle and therefore, it needs a constant supply of oxygenated blood. This is where another type of circulation comes into play, the coronary circulation.
- Coronary circulation is an essential portion of the circulation, where oxygenated blood is supplied to the heart. This is important, as the heart is responsible for supplying blood throughout the body.
- Moreover, organs like the brain need a steady flow of fresh, oxygenated blood to ensure functionality.
In a nutshell, the circulatory system plays a vital role in supplying oxygen and nutrients and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes from the body. Let us gain a deeper insight into the various anatomical structures of the heart:
Structure of the Human Heart
The human heart is a muscular organ that has a unique structure, consisting of several components that enable it to efficiently pump blood. These include the heart wall, heart chambers, blood vessels, and valves. Let’s take a closer look at these components.
Pericardium: The Protective Sac
The heart is enclosed by a double-layered sac known as the pericardium. This structure helps protect the heart from infection and friction while it beats. The outer layer of the pericardium is tough and fibrous, while the inner layer is smooth and lubricated. Between these two layers is a small amount of fluid that reduces friction as the heart expands and contracts.
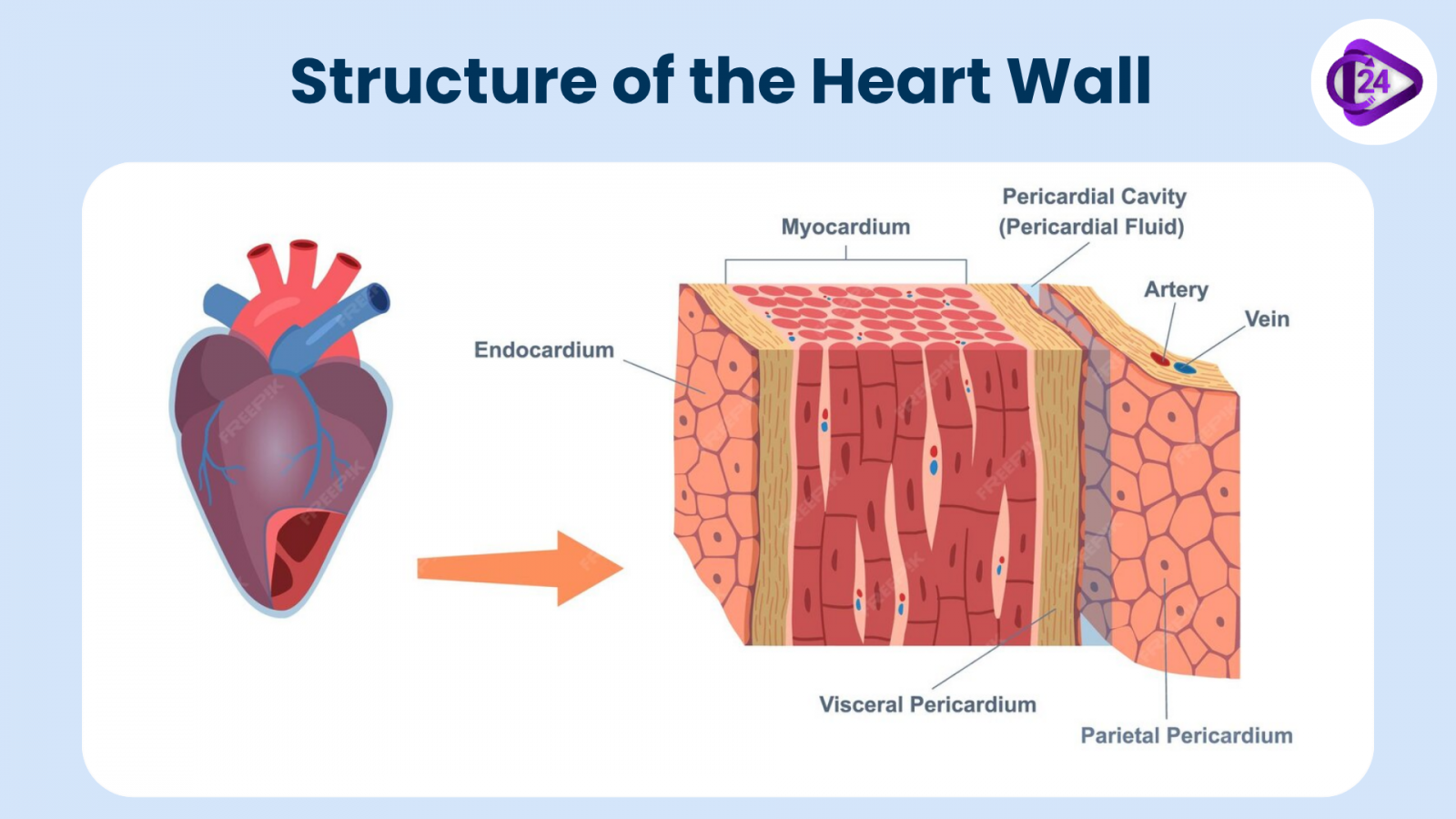
Structure of the Heart Wall
The heart wall consists of three distinct layers:
- Endocardium: The innermost layer that lines the heart chambers and valves. It is smooth and helps prevent blood clots from forming inside the heart.
- Myocardium: The middle layer of the heart, which is the thickest and made up of muscle tissue. It is responsible for contracting and generating the force needed to pump blood.
- Epicardium: The outermost layer that is also part of the pericardium. It helps protect the heart and contains blood vessels that nourish the heart tissue.
Chambers of the Heart
The heart of a human being is made up of four chambers:
- Right Atrium: This is where the body supplies deoxygenated blood through the superior and inferior vena cava to the right atrium.
- Right Ventricle: The right ventricle receives the blood in the right atrium and forces it to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
- Left Atrium: Oxygenated blood is supplied in the lungs through pulmonary veins to the left atrium.
- Left Ventricle: Left atrium supplies the left ventricle which pumps the blood to the body through the aorta. Left ventricle is the strongest because it covers a long distance over which blood has to flow.
Blood Vessels
This heart is attached to a large mouth containing blood vessels which carry blood to and away different parts of the body:
- Aorta: This is the largest artery in the body, in which oxygenated blood flows to the body through the left ventricle.
- Pulmonary Artery: This is the blood that is taken to the lungs where oxygenation is done by the ventricles in the right side of the heart.
- Pulmonary Veins: these veins deliver (oxygenated blood) to the left atrium.
- Superior and Inferior Vana Cava: These are the large veins whereby the deoxygenated blood of the body flows back to the right atrium.
Valves of the Heart
The heart contains four essential valves that ensure blood flows in only one direction, preventing backflow:
- Tricuspid Valve: Located between the right atrium and right ventricle.
- Pulmonary Valve: Found between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
- Mitral Valve: Situated between the left atrium and left ventricle.
- Aortic Valve: Located between the left ventricle and the aorta.
These valves open and close with each heartbeat to maintain efficient circulation.
Facts About the Human Heart
- The heart beats approximately 100,000 times per day, pumping about 70 milliliters of blood per beat.
- On average, the heart pumps about 5 liters of blood every minute, which adds up to over 7,200 liters per day.
- The heart weighs approximately 250-350 grams, with women’s hearts generally being smaller than men’s hearts.
- An average human heart beats 70-75 times per minute when at rest.
- The heart’s left ventricle is the most muscular part, as it pumps blood to the entire body.
Conclusion
The human heart is a wonderful organ, which allows the body to work constantly providing the blood circulation. It has a special structure, chambers, valves and blood vessels, which are specifically designed to assist the body in two forms of circulation and also pump the blood to all parts. The heart, its parts and the circulatory routes are vital to the study of biology or medical examination. It is important to know the major facts and structures regardless of whether it is your first time learning about the heart or taking exams on the matter to get to know the life sustaining processes.




