Daily Quizzes
Mock Tests
No tests attempted yet.
Select Category
Gravitation: The Invisible Force That Shapes Our Universe
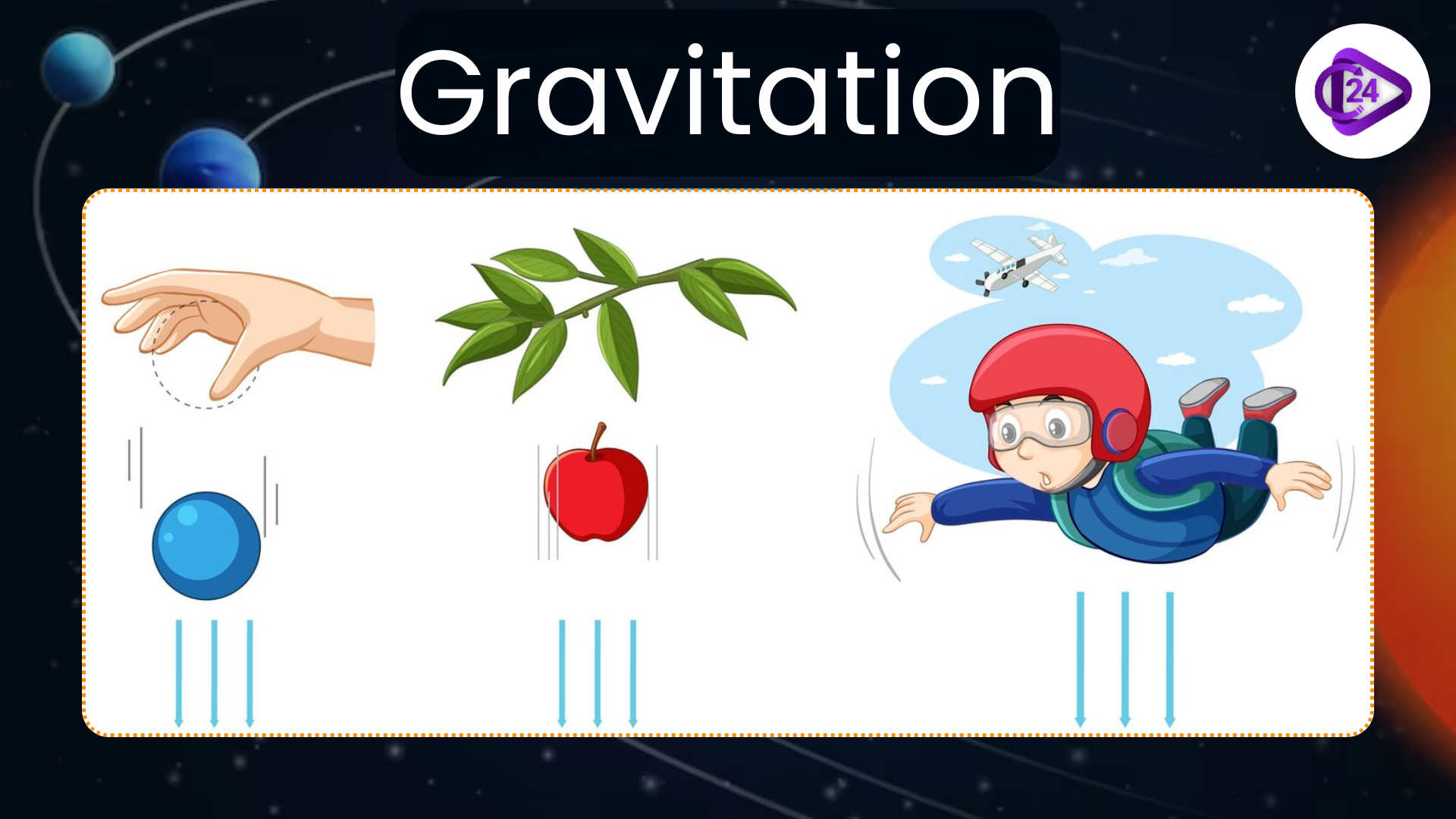
Gravitation is universal force naturally existing and controlling the movement of things in the universe. It is here that the attractive force is responsible because two bodies are attracted toward each other which produces a pull that will depend on the mass of the bodies and the distance between them. This force not only helps keep us in one place to the earth but also is critical in the process of the movement of the celestial bodies like planets, moons, and stars. The sciences of gravitation have greatly developed throughout centuries. One of the earliest mathematicians to explain this force mathematically was Sir Isaac Newton in the late 17th century by his Universal Law of Gravitation.
What is Gravitation?
Gravity or gravitation is the force that pulls two objects towards one another. This force is directly proportional to the mass of the objects and directly proportional to the inverse of the square of the distance between the objects. It is the gravitational attraction between the object and the earth that gives us the weight. The movement of planets around the sun and the movement of the light, time and space is also due to gravity.
The gravitational forces are always attractive compared to the electromagnetic forces which may either repel or attract. It is this attraction that makes the objects to move towards the center of the Earth and is the reason why the celestial bodies remain in contact with each other due to their attraction.
History of Gravitation
Early Theories of Gravity
The concept of gravity can be traced back to the ancient societies, although the formulation was not realized until the efforts of such early scientists as Galileo Galilei and Isaac Newton. According to ancient Greek philosophers (i. e. Aristotle), objects descended to the Earth due to the innate will to go back to the ground. Nevertheless, these initial theories were not scientifically rigorous.
The Law of Universal Gravitation and Isaac Newton.
The actual revolution in the conception of the concept of gravity was achieved in the late 17 th century through the contributions of Sir Isaac Newton. Newton came up with the law of universal gravitation which held that all masses have a pulling force on all masses. This force is dependent on two items; the mass of the items and the distance between them.
Mathematically, the law of universal gravitation of Newton is put as follows:
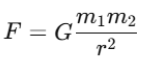
Where:
- F is the gravitational force between two objects.
- G is the gravitational constant, a fundamental physical constant.
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects,
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects.
This law not only explained the motion of objects on Earth but also described the orbits of the planets and the motion of celestial bodies, providing a universal framework for understanding gravity.
Albert Einstein and General Relativity
While Newton’s laws worked well for most practical purposes, they could not explain certain phenomena, such as the motion of Mercury's orbit or the bending of light around massive objects. This led to Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity, proposed in 1915, which revolutionized our understanding of gravity.
The concept of spacetime curvature replaced the concept of force of gravity as provided by the theory that was introduced by Einstein. General relativity is founded on the fact that the family of the mass bends time and space, and items travel along the paths. This theory was determined to provide improved predictions compared to that of Newton particularly at the extreme gravitational fields.
The Law of Universal Gravitation and Acceleration Due to Gravity
Most of the gravitational phenomena continue to be based on the law of gravitation as formulated by Newton. But another one that should also be learned is the acceleration due to gravity (g), which refers to how objects fall on earth due to the influence of gravity.
Acceleration Due to Gravity (g)
It is the rate at which objects accelerate when they fall towards Earth under the influence of gravity. It is represented by 'g' and is approximately 9.8 m/s² near the Earth's surface. This means that every second, the velocity of a falling object increases by 9.8 meters per second. All objects experience the same acceleration due to gravity, regardless of their mass, when air resistance is not considered.
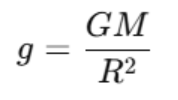
Where:
- G is the gravitational constant.
- M is the mass of Earth,
- R is the radius of Earth.
At higher altitudes, such as in space or on mountaintops, the value of g decreases because the distance between the object and the center of Earth increases.
Variation of g with Height and Depth
1. Above the Earth’s Surface (Height):
As an object moves higher from the Earth's surface, the value of g decreases. This can be calculated using the formula:
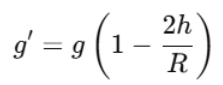
Where hhh is the height above Earth’s surface and RRR is the radius of Earth.
2. Below the Earth’s Surface (Depth):
Inside the Earth, gravity also decreases with depth. The formula is:
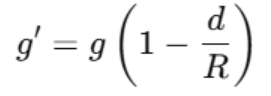
Where ddd is the depth inside Earth and RRR is the radius of Earth.
Gravitational Fields and Potential
Gravitational fields explain the effect a huge body exerts on the surrounding space. The gravitational field at any point in space is the amount of force the small test mass would feel at that point, which is divided by the unit mass of the test mass.
The amount of potential energy per unit mass at a point in a gravitational field is referred to as the gravitational potential. In the case of the point mass, the gravitational potential V at a distance r of the mass
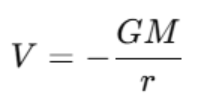
Where:
- M is the mass creating the gravitational field,
- r is the distance from the center of the mass.
Applications of Gravitation: Satellites and Space
Gravitation plays a key role in the motion of satellites, space exploration, and other astronomical phenomena. Let’s look at some important concepts related to satellites:
Orbital Velocity
The orbital velocity is the speed an object must travel to maintain a stable orbit around a planet. For Earth, the orbital velocity vvv is given by:
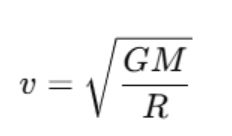
Where:
- G is the gravitational constant,
- M is the mass of Earth,
- R is the radius of the orbit.
Escape Velocity
The escape velocity is the speed required for an object to break free from Earth's gravitational pull. It is given by:
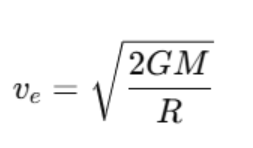
Where:
- M is the mass of Earth,
- R is the radius of Earth.
This is the minimum velocity required for an object to escape Earth’s gravity without further propulsion.
Satellite Energy and Weightlessness
Kinetic energy plus potential energy of an orbiting satellite are equal to its energy. This is because astronauts feel weightless in space because they are in a state of free fall which simply means that they are constantly falling to the earth but falling very fast so that it can sustain an orbit.
Key Formulas for Revision
Here are some essential gravitational formulas to remember:
- Gravitational force:
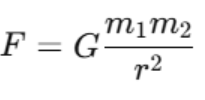
- Acceleration due to gravity:
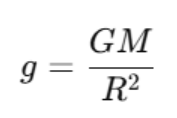
- Gravitational potential:
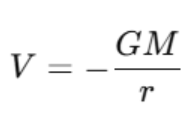
- Orbital velocity:
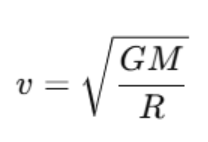
- Escape velocity:
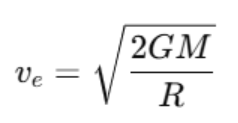
The Gravitational Research and Expanding Universe
Gravitation does not only play a central role in the movement of the planets but also in the expansion of the universe. Although the matter is being drawn towards itself by gravity, the universe is also expanding as a result of the Big Bang. In 1927-1931, Georges Lemaitre (the Father of the Big Bang Theory)proposed the concept of an initial point of concentrated mass, suggesting the origin of space and time.
Research on gravity is on the rise and scientists are researching on gravitational waves and attempting to solve the problem of general relativity versus quantum mechanics so that they can devise one theory of everything.
Conclusion
Gravitation is a force that regulates movement of all items whether the smallest particle or even the heaviest heavenly bodies. Gravity affects how things behave, be it a fall of an apple on the earth or the movement of galaxies in the universe. As more studies are conducted on the study of the gravitational waves and quantum gravity, then we will just have a better insight on this force and this will further reveal more about the nature of the universe.




